Medical personnel awareness of organ donation is key success in health service area 7, Thailand
Somkrit Sripontan1, Walaipon Pukkaeraka1, Suchanya Dejsiri 1.
1Surgery, Mahasarakham hospital, Mahasarakham, Thailand
the one study group.
Introduction: Organ donation has become a key health policy in Thailand, aiming to foster a new culture of post-mortem donation, particularly from brain-dead and cardiac-dead patients.Thailand’s Health Service Area 7, which comprises hospitals across four provinces (Roi Et, Khon Kaen, Maha Sarakham, and Kalasin), has collaboratively launched initiatives starting with hospital medical staff and gradually expanding into the broader community. Over two years, these efforts led to significant improvements across all donation modalities: organ donations increased from 16 to 44 cases, eye donations from 19 to 55 cases, and donor card registrations rose dramatically from 2,981 to 16,296.
Method: We revised protocols and redefined the responsibilities of healthcare personnel at all levels. Leadership teams include physicians and transplant coordination nurses (TCNs), who organize annual conferences to revise and update procedures. Targeted small-group meetings are held in key wards to appoint transplant coordination ward nurses (TCWNs), and local leaders and community health volunteers are involved in communicating with patients’ families. Regional hospitals assist with public awareness campaigns, donor card registration, and participation in cremation ceremonies. We also collaborate with local influencers—including singers, models, and executives of R7—to raise public awareness. To foster respect and gratitude toward donors, we honor them at every stage of the process. This includes bedside religious rituals, ceremonial recognition by the hospital’s executive team, and attendance at the donor’s funeral. These respectful practices help build trust, empower families, and shift community perceptions, ultimately cultivating a new culture of organ donation.
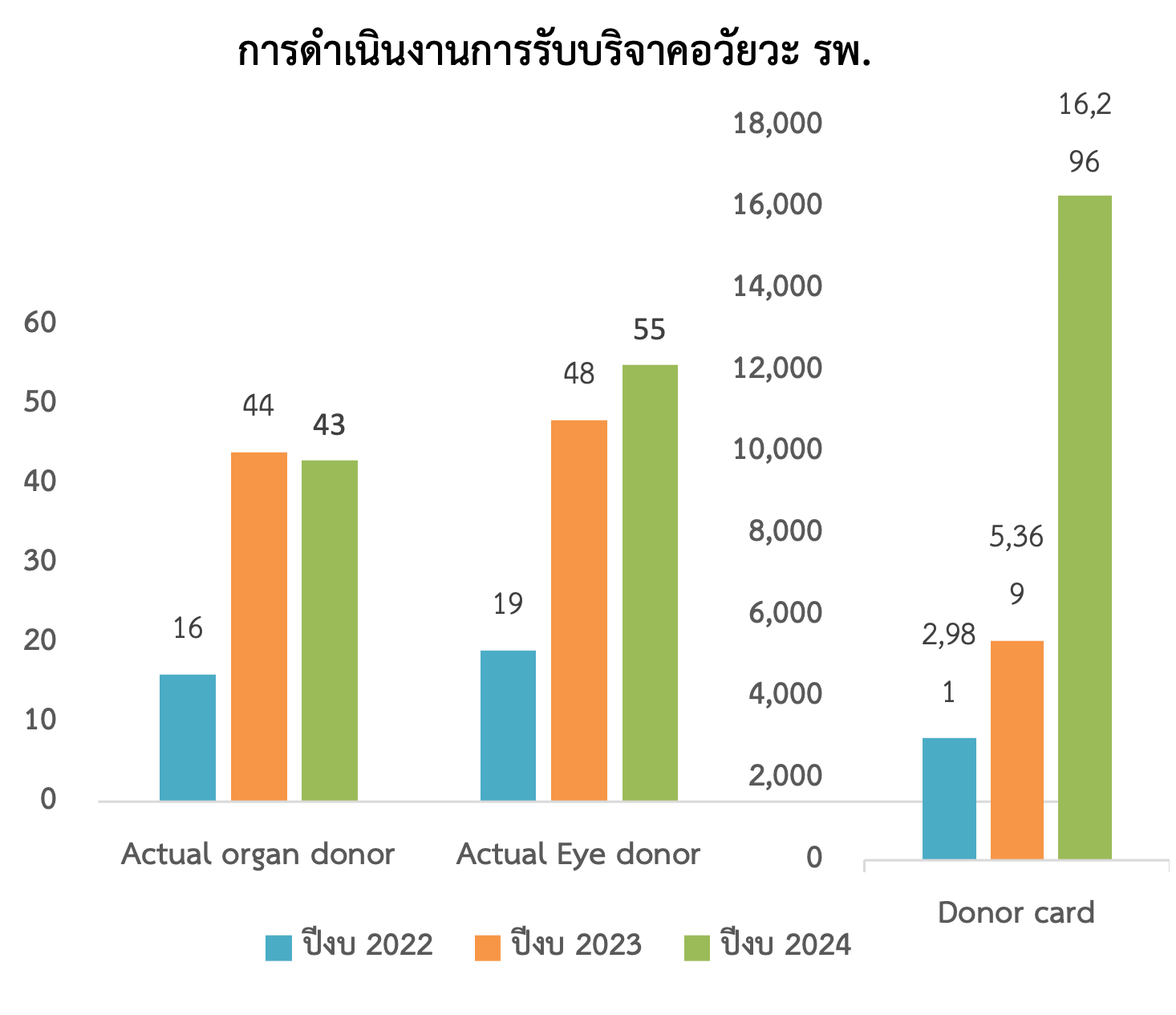
Results: Statistical Results: Organ donation cases significantly increased in 2023 and 2024, with 44 and 43 successful donations respectively. Eye donations also saw a marked increase—48 cases in 2023 and 55 in 2024. The number of registered donor cards increased notably, making it easier for families and medical personnel to make donation decisions in critical moments.
Non-Statistical Results: Community health volunteers and nurses, who maintain close relationships with the local population, play a vital role in educating families about the value of donation and reducing fears related to spiritual beliefs about organ loss in the afterlife. Public outreach through informational booths at temples, schools, local festivals, and hospitals has helped introduce and normalize the culture of organ donation in the wider community.
Conclusion: The collaboration of hospitals within Health Region 7 has proven effective in improving outcomes. The active participation of healthcare workers at every level, sharing knowledge and promoting organ donation as a shared cultural value, has been a key factor in our success.
Mahasarakham hospital .
[1] organ donation policy