Ex vivo delivery of autologous regulatory T cells during normothermic machine perfusion in porcine kidney transplantation
Masataka Kawamura1,2, Yuki Noguchi2, Catherine Parmentier2, Samrat Ray2, Shigeaki Nakazawa1, Yoichi Kakuta1, Lisa Robinson3, Markus Selzner2.
1Department of Urology, The University of Osaka, Osaka, Japan; 2Division of General Surgery, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada; 3Division of Nephrology, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, Canada
Introduction: Kidney transplantation is the optimal treatment for end-stage kidney disease. However, ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) remains a significant challenge, particularly in marginal grafts, as it contributes to delayed graft function and antibody-mediated rejection. Regulatory T cells (Tregs), a subset of CD4+CD25+ T cells, play a central role in modulating immune responses and have been shown to ameliorate ischemic acute kidney injury.
Method: Normothermic ex vivo kidney perfusion (NEVKP) is a promising platform for organ preservation and therapeutic intervention, allowing for targeted delivery of Tregs directly to the kidney. In this study, we isolated and expanded Tregs from porcine peripheral blood and administered them during NEVKP in a porcine autotransplantation model.
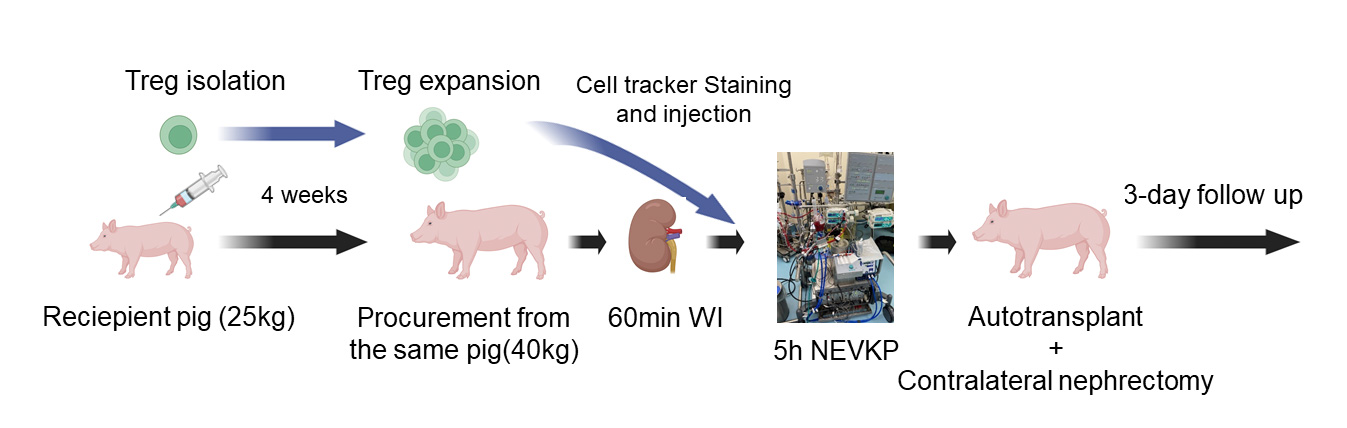
Results: Tregs administered during perfusion showed potential to suppress local immune responses without systemic immunosuppression. Foxp3-positive cells increased in the graft tissue, while effector T cells were suppressed immediately post-transplant. Although histological changes were not statistically significant, there was a trend toward reduced tubular injury. These findings suggest that Tregs delivered during NEVKP could mitigate IRI and enhance graft preservation.
Conclusion: This study provides the first evidence in a large animal model supporting the feasibility and potential of Tregs for localized immunomodulation during kidney transplantation, paving the way for future studies targeting rejection.
[1] Machine perfusion
[2] Normothermic
[3] Regulatory T cells
[4] Kidney transplantation
[5] Pig