Participation of a donation nurse in family donation conversations is associated with higher rates of family consent to donation irrespective of who leads the conversation
Michael O'Leary1, McDonald Mark2, Cavazzoni Elena1.
1Organ and Tissue Donation Service, New South Wales Health, Kogarah, Australia; 2Organ and Tissue Authority, Government of Australia, Canberra, Australia
Introduction: Australian and international data has shown that involving a donation specialist in a family donation conversation (FDC) is associated with higher family consent rates irrespective of donor age [1, 2]. In Australia a key performance indicator is to achieve 100% donation specialist nurse (DSN) participation in FDCs, and this is tracked using the DonateLife Audit (DLA). In NSW however, we also audit FDCs in a Referral Log (RL), where auditors are asked to indicate the designation of the person that “led” the FDC. We investigated whether the benefit of DSN presence in an FDC required them to be the leader of the conversation. For the purposes of the study only FDCs occurring after hospital staff rather than family raised organ donation were explored, as these FDCs are often associated with the lowest consent rates.
Method: We identified FDCs occurring in NSW DonateLife Network hospitals in 2022 - 2024 after hospital staff first raised donation, from both the DLA and the NSW RL, and determined the consent rate to donation when a DSN was listed as participating in the conversation (DLA) or leading the conversation (RL).
Results:
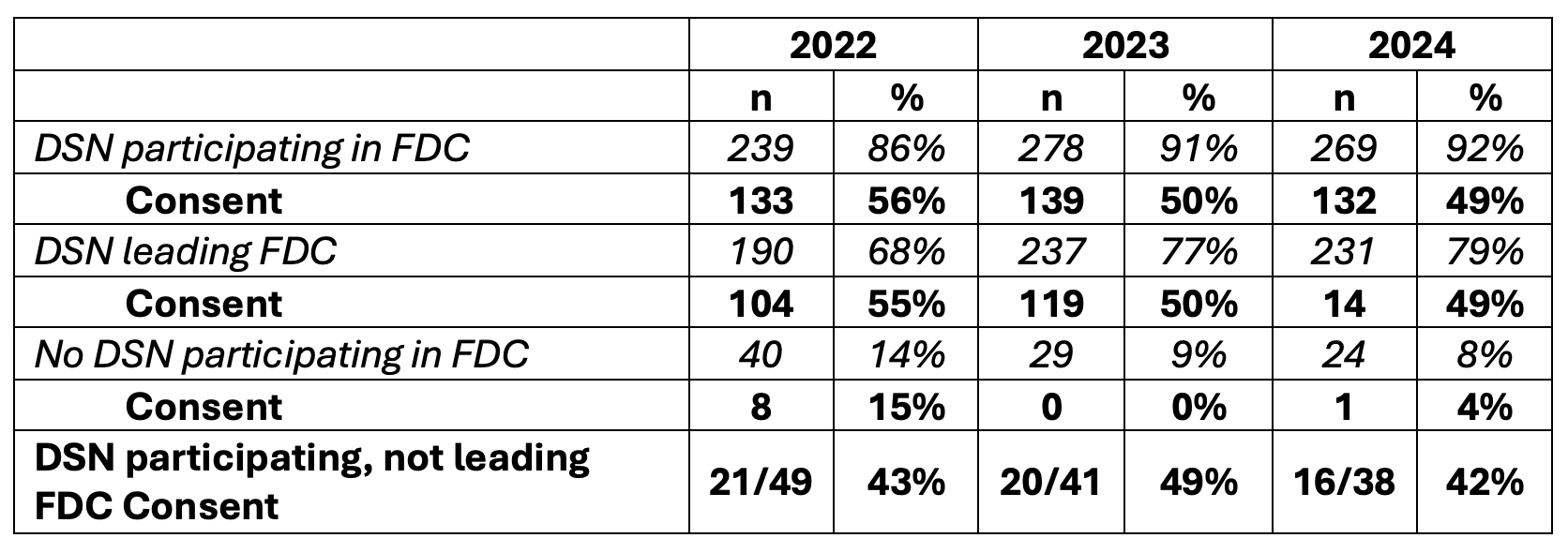
Conclusion: We found that there was only a small decrement in consent rate in staff-raised FDCs when DSNs indicated that they were participating but not leading the conversation. The positive effect of DSNs in FDCs is most likely related to their participation (collaborative conversation), rather than a requirement to lead the FDC. ICU teams should continue to implement collaborative FDCs to ensure families are provided with information to enable them to make an informed consent decision.
References:
1. The impact of organ donation specialists on consent rate in challenging organ donation conversations. Radford S, D'Costa R, Opdam H, et al. Crit Care Resusc. 2023;22:297-302.
2. Reading the family: A constructivist grounded theory on organ donation conversations. Avilés L. PLoS One. 2024;19:e0312462.
[1] Organ donation specialist nurse
[2] Family donation conversation
[3] Family consent